The world of investing can be complex, with a myriad of options available to investors of all levels (invetsing 5). Two of the most popular investment vehicles are mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). While both offer a way to diversify your portfolio and potentially grow your wealth, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different investor profiles. Let’s delve into the key differences between mutual funds and ETFs to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Mutual Funds
A mutual fund is a pool of money collected from multiple investors and invested in various securities like stocks, bonds, or other assets. It is managed by a professional fund manager who makes investment decisions on behalf of the investors. Mutual funds are typically categorized as either actively or passively managed.
- Actively managed mutual funds: These funds employ fund managers who actively research and select securities in an attempt to outperform a specific benchmark. While active management offers the potential for higher returns, it also comes with higher fees due to the expertise involved.
- Passively managed mutual funds (index funds): These funds aim to replicate the performance of a particular market index, such as the S&P 500. They typically have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds.
Understanding ETFs
An ETF is a type of investment fund that tracks an underlying index, sector, commodity, or other asset. Unlike mutual funds, ETFs trade on stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell them throughout the trading day. ETFs are generally passively managed, mirroring the performance of their underlying index.
Key Differences Between Mutual Funds and ETFs
| Feature | Mutual Funds | ETFs |
| Trading | Once a day, after the market closes | Throughout the trading day |
| Management Style | Actively or passively managed | Primarily passively managed |
| Fees | Generally higher expense ratios | Typically lower expense ratios |
| Minimum Investment | Varies by fund | Usually lower, as you buy individual shares |
| Tax Efficiency | Can be less tax-efficient due to frequent trading | Often more tax-efficient |
Which is Right for You?
The choice between mutual funds and ETFs depends on several factors, including your investment goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment knowledge. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide:
- Investors seeking active management: If you believe in the ability of a fund manager to outperform the market, actively managed mutual funds might be suitable. However, be prepared for higher fees.
- Investors seeking low-cost diversification: ETFs are generally a good choice for investors looking to build a diversified portfolio at a low cost. Their passive management style and tax efficiency make them attractive options.
- Investors who prefer frequent trading: ETFs offer the flexibility to buy and sell throughout the trading day, making them suitable for investors who want to actively manage their positions.
- Investors with limited investment capital: ETFs often have lower minimum investment requirements, making them accessible to investors with smaller amounts of money.
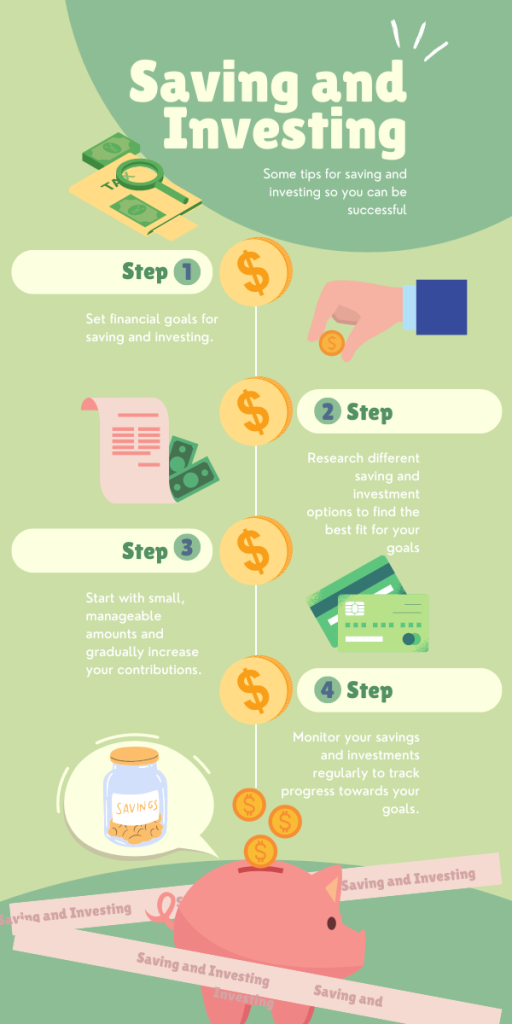
It’s essential to conduct thorough research or consult with a financial advisor before making investment decisions. Understanding your financial goals and risk tolerance is crucial in selecting the right investment vehicle for your portfolio.
Remember: Diversification is key to managing investment risk. Consider incorporating both mutual funds and ETFs into your portfolio to achieve your financial objectives.
By carefully evaluating your investment preferences and considering the factors discussed above, you can make an informed decision about whether mutual funds or ETFs are the better fit for your financial journey.