Investing your money is a crucial step towards financial security and growth. However, with a myriad of options available, it can be overwhelming to decide where to allocate your funds. Two of the most fundamental investment types are stocks and bonds. While both offer opportunities for returns, they differ significantly in terms of risk, reward, and suitability for different investors.
Understanding Stocks
When you purchase a stock, you become a part-owner of a company. You share in the company’s profits and losses. The value of your investment fluctuates based on the company’s performance, economic conditions, and overall market trends.
Key characteristics of stocks:
- High potential returns: Stocks have historically outperformed other investment classes over the long term, offering the potential for significant capital appreciation.
- High risk: Stock prices can be volatile, and there’s a risk of losing your entire investment if the company fails.
- Dividends: Many companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders as dividends, providing a regular income stream.
- Liquidity: Stocks are generally highly liquid, meaning they can be easily bought and sold.
Understanding Bonds
Unlike stocks, bonds represent a loan to a company, government, or municipality. When you buy a bond, you’re essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of your principal at maturity.
Key characteristics of bonds:
- Lower potential returns: Bonds typically offer lower returns compared to stocks, but they are generally considered less risky.
- Lower risk: Bonds are generally considered safer than stocks because bondholders have a prior claim on assets in case of bankruptcy.
- Fixed income: Bonds provide a steady income stream through regular interest payments.
- Maturity date: Bonds have a specified maturity date, at which point the issuer repays the principal.
Which Investment is Right for You?
The choice between stocks and bonds depends on your individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Consider investing in stocks if:
- You have a long-term investment horizon.
- You’re comfortable with market volatility.
- You’re seeking higher potential returns.
- You’re willing to diversify your portfolio across different companies and industries.
Consider investing in bonds if:
- You have a shorter investment horizon.
- You prioritize income and stability over high growth.
- You’re risk-averse.
- You want to balance the risk in your portfolio.
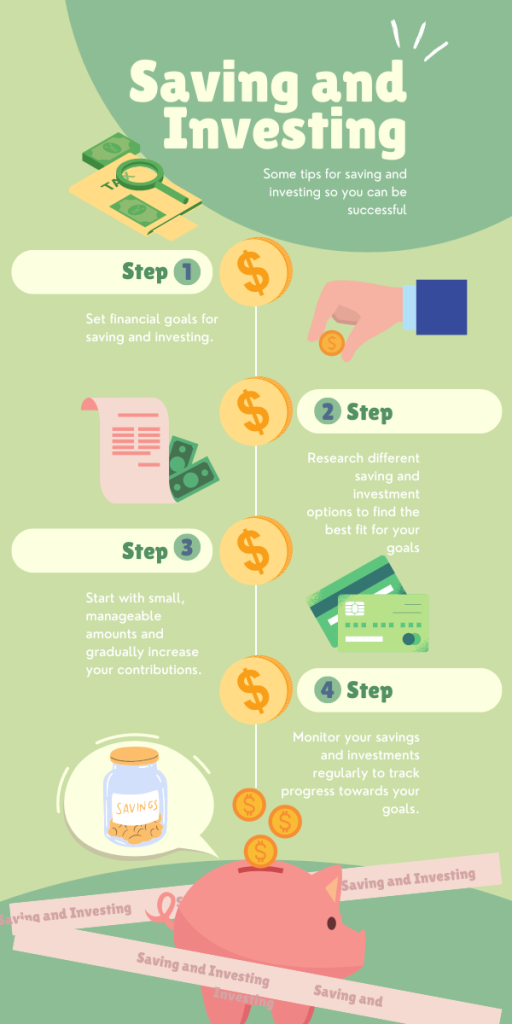
Balancing Your Portfolio
Most financial advisors recommend a diversified portfolio that includes both stocks and bonds. This approach helps to manage risk while maximizing potential returns. The optimal mix of stocks and bonds will vary depending on your individual circumstances.
Factors to consider when building your portfolio:
- Your age: Younger investors can generally tolerate more risk and may allocate a higher percentage of their portfolio to stocks.
- Your risk tolerance: Assess your comfort level with market fluctuations.
- Your financial goals: Determine your investment objectives, such as retirement savings, education funding, or purchasing a home.
It’s essential to conduct thorough research or consult with a financial advisor before making investment decisions. Understanding the fundamental differences between stocks and bonds is a crucial first step toward building a well-rounded investment portfolio that aligns with your financial aspirations.